Introduction
For the release of IGB 6.5, we have created a Sequence Viewer. This pop-up window will allow a clean view of the sequence that a user selects; when the genomic sequence of a gene model is chose, the exons and introns are shown in different colors, but the viewer can also be set to show cDNA from the model. Start and stop codons are shown, when the information is available, and the viewer allows all possible translations. The data can be copied into a text file or exported as a fatsa file, making this viewer a helpful and convenient tool for examining either a gene model or a user-defined area of sequence.
Viewing a Gene Model/ Annotation
For gene models/ annotations, simply right click on the annotation. You can chose an individual exon to view, or you can Select Parent and then right click again to view the whole gene model; chose Show genomic sequence.
This will immediately open the Sequence Viewer (see picture below). In the Viewer, exons will be shown in yellow and introns will be shown in white. If a single exon was chosen, it will appear in yellow. The start codon (ATG) is shown with a green box around it, and the stop codon has a red box around it.
If this color scheme is difficult for a user, the Change color scheme button will invert the black and white, and change the yellow to blue.
The title of the viewer window will indicate what gene model/ element it is showing. In our example, this data is the A_thaliana_Jun_2009 genome version, and specifically the TAIR10 mRNA. The gene we are looking at is on chromosome 1, it's ID is AT1G07350.1 and it is on the minus strand.
cDNA and Translation
After selecting a gene model, the Sequence Viewer allows you to select Show cDNA only, which will eliminate exons from the shown sequence. We recommend selecting this option before using the translation feature. If an individual exon is selected, this button will be available, but will not change the sequence.
After selecting this feature, your sequence will show as completely yellow (blue) and the button will change to Show complete.
Translation options are accessed from the Show menu and include:
The translation appears over the sequence:
Viewing Selected Sequence
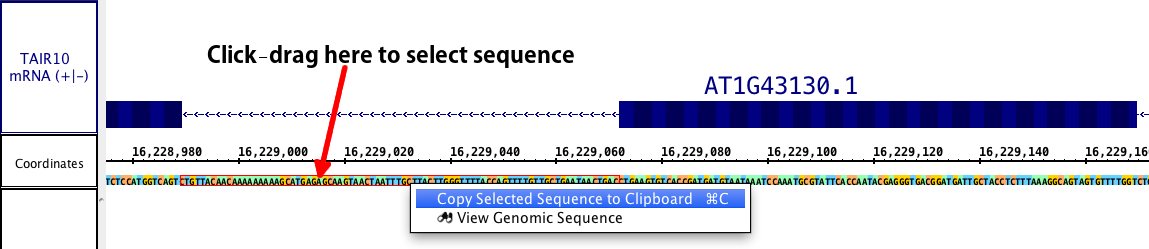
IGB also allows you to directly select genomic DNA sequence to view. While this method loses the advantage of annotations/ exon designations, it does allow you to select DNA from introns, upstream and downstream regions, or any other area which may contain sequence of interest (i.e. promoters, enhancer binding elements, etc.). The first step is to ensure the sequence is loaded (Data Access tab > Load All Sequence button OR > Load Sequence in View button). Select the sequence you wish to view by click-dragging the cursor over the sequence bar at any zoom level. A red outline will appear around the selected sequence.
Right click within the selected area and chose Show genomic sequence. The sequence viewer will open as before, although the title will now show that this window has genomic sequence, the genome version, chromosome number and the range covered by the sequence. The Show cDNA only option will be disabled, but all other options will remain. The DNA sequence will always be presented in the + (plus) direction. However, if your sequence of interest is the other strand, Show > Reverse Complement will provide the reverse complement of the sequence.
This method of genomic DNA selection also allows a direct copy to the clipboard, if you wish to skip the Sequence viewer. Simply right click within the selected sequence, and chose Copy.
Copying and Saving Sequence
You can copy a selection or all of your sequence; highlight the sequence of interest (or all of the sequence) and use Edit > Copy selected sequence to clipboard. The open a text editor of choice and paste the sequence.
Another option is to save the sequence to a fasta file, using File > Save as Fasta. The fasta file will contain a line with all of the relevant information, the same as seen in the title of the viewer window. fasta files can be used for many bioinformatics purposes; they can additionally be opened in most text viewers as well, allowing a quick way to access the whole sequence with the relevant data set information.