| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
IGB display reference genomic sequence in the Coordinates track. IGB supports many interactions and views on genomic sequence, including copy copying sequence, viewing sequence in a specialized the Sequence Viewer window, and morerunning BLAST searches. Other features may be available via IGB plug-ins.
Loading reference genomic sequence data
IGB does not load genomic sequence into the viewer until requesteduntil you request it, giving you total control over how much data is loaded and when.
To load genomic sequence
...
Sequence data will then load from a remote data source or local file, depending on the whether you're viewing a genome version supported by an external data source or if you're viewing a genome you loaded using the Load Custom Genome option.
| Tip |
|---|
If you are working with a genome that is not supported by the IGBQuickLoad data source, let us know. It is easy to add new genome versions to IGBQuickLoad.org. |
| Warning |
|---|
Some partial external sequence data servers will reject requests for residues from a region that is too large. Others will return the data, but only after a very long wait. If you have problems, let us know. |
What to do if your genome is not supported
If you have a sequence file in one of the formats that IGB can read (File Formats), you can use that sequence as a reference sequence.
...
- Choose File > Open Custom Genome
- Enter a species name into the Species text box
- Enter a genome version name into the Genome Version text box
- Use the "..." button to browse and open your reference sequence file
- Click OK in the Open Custom Genome window
IGB will then open the file and it will appear in the Data Management table.
...
| Note |
|---|
If the sequence length contradicts your annotation files, IGB will not be able to display them together. Please contact us through the forums if you need help. |
Loading sequence into a new track
If you want to load an additional sequence as a track rather than as a reference sequence (perhaps a substrain or an individual), open it as if it were an ordinary file.
...
As with any other track, a new empty track will appear labeled with the name of the file you opened. The file name will appear in the Data Management table in the Data Access tab.
Viewing the reference sequence
At low zoom (many bases are shown) loaded sequence is shown as a gray bar beneath the coordinates axis.
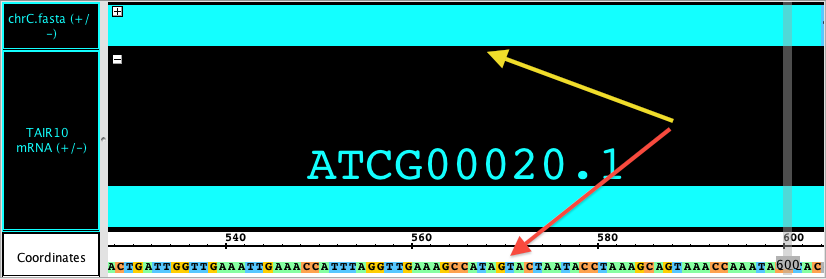
When you are zoomed in, the sequence bases become visible. If sequence has not yet been loaded, '-' (hyphen) character characters are shown. If the sequence is loaded, the nucleotides are shown using the letters A, T, G and C or N to represent positions with an unknown basenucleotide base letters are shown. By default, IGB uses cool colors to represent A and T bases and warmer colors to represent G and C bases.
Change base colors in the Preferences > Other Options tab.
| Info |
|---|
Note that depending on the sequence data server, file, or URL that supplied the sequence data, bases may appear in upper or lower case. |
Examples
In the first image, you can see a sequence loaded as a track (red arrow). Notice that the refseq has not yet been loaded (blue arrow) so it appears gray with '-' marks; when you are zoomed out, the sequence track shows a gray bar (default color), and the coordinate axis is empty.
...
After loading the refseq (red arrow), the sequence in the track (yellow arrow) changes to the FG color for that track (cyan in this case) where ever it matches the refseq. In this state, it will only highlight differences/mismatches with a letter and a color change. Zoomed out, the track appears as a solid bar in the FG color for the track. The refseq appears as a gray bar in the coordinate axis.
Copy and paste sequence bases in IGB
You can copy a sequence of bases into another application, such as Notepad.
...